Climate change is significantly increasing the risk of zoonotic disease outbreaks, including pandemics, by influencing both vector-borne and non-vector-borne transmission pathways. The comment published in Lancet Planet Health 2025 highlights that current research reveals a heavy focus (76.5%) on climate-sensitive, vector-borne diseases like malaria, dengue, and Lyme disease.
In contrast, less attention has been given to non-vector-borne zoonotic diseases (e.g. Ebola, Nipah, rabies), despite their well-known pandemic potential. This research imbalance likely stems from the complexity of studying cross-species viral spillover, rather than a weaker climate connection.
Key frameworks such as the One Health Joint Plan of Action (2022–26) and the UNEP’s Preventing the Next Pandemic recognize the climate–zoonosis link. However, others (e.g. WHO’s Global Strategy on Health, Environment, and Climate Change) do not fully address it. Although the recently adopted Pandemic Agreement supports the One Health approach, the explicit integration of climate change remains limited.
Recent progress includes recognition of the health impacts of climate change in global forums like COP28 (2023) and the World Health Assembly (2025), which adopted the Global Action Plan on Climate Change and Health (2025–28). These developments acknowledge the climate crisis as a public health emergency.
The comment call for greater attention in research to understand how climate change affects zoonotic disease dynamics, including wildlife-pathogen interactions, biodiversity, pathogen evolution, and cross-species transmission. A deeper understanding is essential for effective prevention, surveillance, and incorporation of climate considerations into international health regulations.
Read the Comment here: Climate change and pandemics: a call for action
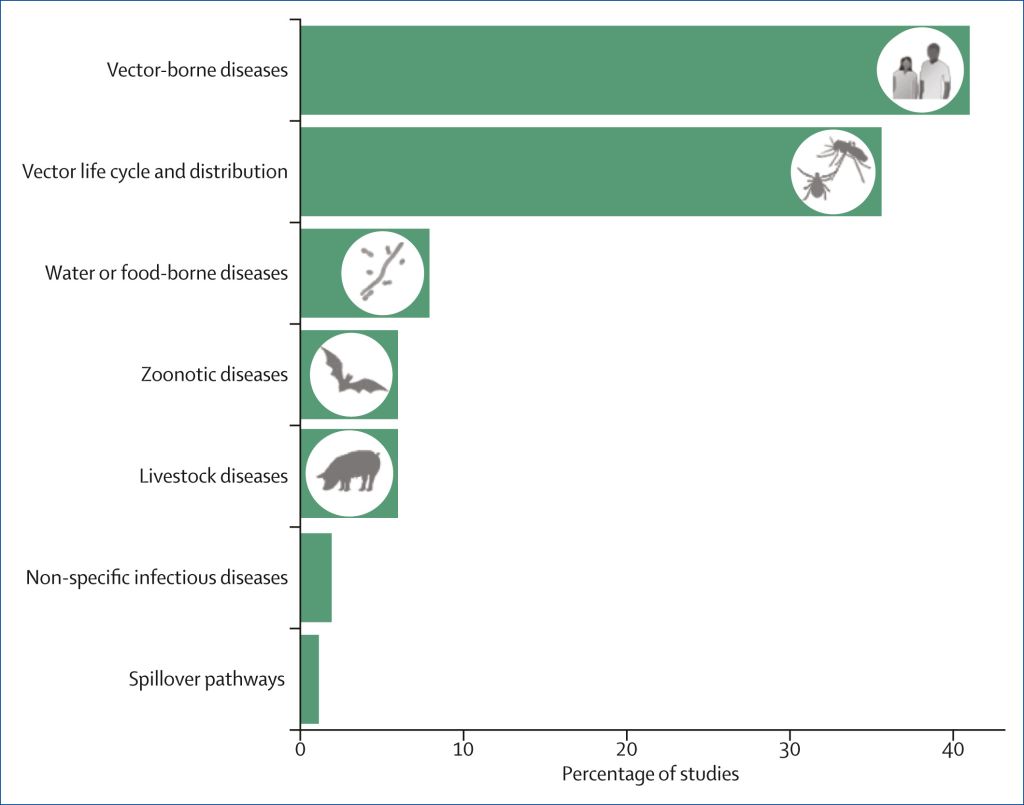
Figure: Research publications examining the effect of climate change on infectious diseases (PubMed, from Jan 1, 2010, to Sept 20, 2024, N=1014)









